Basic Engineering
Once the concept has been selected and the technical scope of the plant has been determined for the first time, all expected costs and expenses are determined in basic engineering.
What exactly does Basic Engineering involve?
Basic engineering at DMT ENCOS includes a multitude of activities. The extent depends largely on the project framework and thus on the product to be produced. Furthermore, the know-how to be applied regarding the manufacturing process of the plant to be used is crucial for the necessary planning effort within basic engineering. The most important and recurring performance steps are explained in detail below.
From process development to large-scale plants
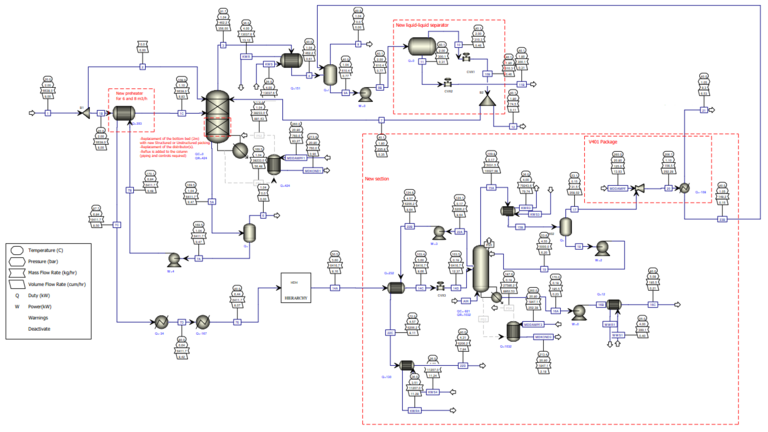
The selected procedure determines the type and necessary sequence of the basic process operations. For the representation of a process engineering procedure, so-called basic flow diagrams are created in basic engineering and discussed further in the planning phase for further coordination.
In the basic flow diagram, the reactants are defined and assigned to the corresponding equipment for storage. So-called reaction products, processing steps and their final storage are also included in such a basic flow diagram and are therefore also part of process development. In order to achieve optimum process engineering, the following work steps are necessary in advance:
- Laboratory development (tests on the smallest scale)
- Pilot Plant Reactor
- Pilot plant
- First large-scale plant
In order to limit the time and material expenditure as much as possible, DMT ENCOS also uses appropriate simulation programs in plant planning, e.g. ASPEN, in order to be able to calculate the respective basic process engineering operations.
Material, mass and enthalpy balances regulation as the central task of a process engineer
The conceptual design of a process engineering plant is the responsibility of the process engineer. The focus is to design a plant in a way that its investment and the operating costs are balanced while simultaneously maintaining the required product properties with regard to quantity and quality. In order to achieve this task, the material, mass and enthalpy balances for the individual process stages as well as for the future overall plant must be established. The so-called plant boundaries provide an assistance to further determination of raw material and energy consumption as well as product and waste quantities.
Within the process engineering plant, the balances determine the quantity flows and their physical/chemical states to be observed. The results from the development of the mass and energy balances are then documented in the mediums data sheets.
The creation of basic and process flow diagrams as one of the basic tasks of DMT ENCOS
Flowcharts are among the most important documents in the field of basic engineering. They are generated in three levels of detail:
- Basic Flow Diagram
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
- Piping and instrument flow diagram (Process and Instrumentation Diagram / P&ID)
While basic and process flow diagrams have to be created as part of basic engineering, the more detailed piping and instrument flow diagrams (P&IDs) are only processed in the subsequent phase (execution of the plant) as part of the detailed engineering. For the creation of the flow diagrams, either client specifications are given or they are agreed between the planner and the operator. The process flow diagram is used to illustrate the process engineering concept and thus represents the next higher level of detail work to the basic flow diagram. All essential components can be found here:
- Pumps, compressors, heat exchangers
- Columns, containers
- The main piping and transport equipment
- Measuring and control Equipment
What is part of the material concept?
Before DMT ENCOS starts designing the main apparatuses, the materials to be used in the future process must be defined and documented. The selected materials not only influence the existing design and construction of the pipelines and equipment, but also their procurement costs.
Special attention must be paid to material design, as warranty claims must also be able to withstand the corresponding stresses of corrosion and usage for a long time. In this regard, DMT ENCOS engineers rely on their many years of experience in strength, corrosion and usage behavior analysis. After concluding to the material concept, the following points must be taken into account by the process engineers:
- Design pressures and temperatures
- Strength aspects
- Weldability of the proposed material
- Technical aspects of production
- Flexibility against changes (nozzle adaptations, retrofitting)
We are looking forward to your inquiry.
Buxtehuder Straße 29
D-21073 Hamburg
Tel.: +49 40 751158-0
Fax: +49 40 751158-30
sales@encos.de